Page 5 - reflections_dyslipidaemia_newsletter5_2023
P. 5
REFLECTIONS
Dyslipidaemia
Dyslipidaemia Global Newsletter #5 2023
Dyslipidaemia
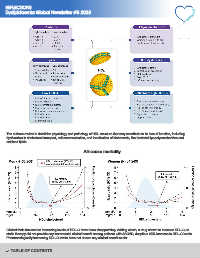
The authors review in detail the physiology and pathology of HDL structure that may contribute to its loss of function, including
dysfunction in cholesterol transport, cell communication, and inactivation of biohazards, like bacterial lipopolysaccharides and
oxidized lipids.
All-cause mortality
Clinical trials focused on increasing levels of HDL-C have been disappointing. Adding niacin, a drug shown to increase HDL-C, to
statin therapy did not provide any incremental clinical benefit among patients with ASCVD, despite a 25% increase in HDL-C levels.
Pharmacologically increasing HDL-C levels have not shown any clinical benefit so far.
TABLE OF CONTENTS